HSC-T: B-ultrasound-to-elastography Translation via Hierarchical Structural Consistency Learning for Thyroid Cancer Diagnosis
Abstract
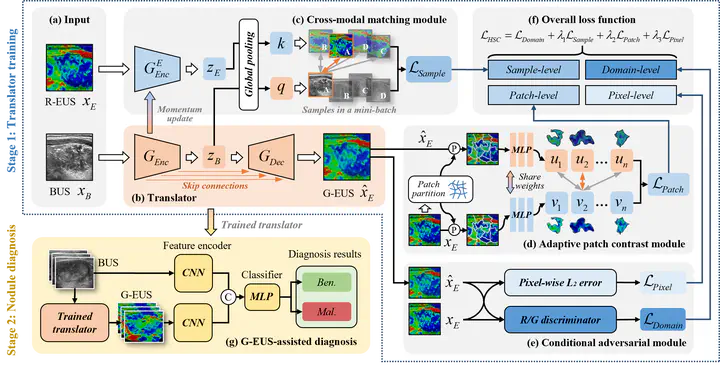
Elastography ultrasound imaging is increasingly important in the diagnosis of thyroid cancer and other diseases, but its reliance on specialized equipment and techniques limits widespread adoption. This paper proposes a novel multimodal ultrasound diagnostic pipeline that expands the application of elastography ultrasound by translating B-ultrasound (BUS) images into elastography images (EUS). Additionally, to address the limitations of existing image-to-image translation methods, which struggle to effectively model inter-sample variations and accurately capture regional-scale structural consistency, we propose a BUS-to-EUS translation method based on hierarchical structural consistency. By incorporating domain-level, sample-level, patch-level, and pixel-level constraints, our approach guides the model in learning a more precise mapping from BUS to EUS, thereby enhancing diagnostic accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method significantly improves the accuracy of BUS-to-EUS translation on the MTUSI dataset and that the generated elastography images enhance nodule diagnostic accuracy compared to solely using BUS images on the STUSI and the BUSI datasets. This advancement highlights the potential for broader application of elastography in clinical practice.
Add the publication’s full text or supplementary notes here. You can use rich formatting such as including code, math, and images.